MySQL Architecture
MySQL’s Logical Architecture
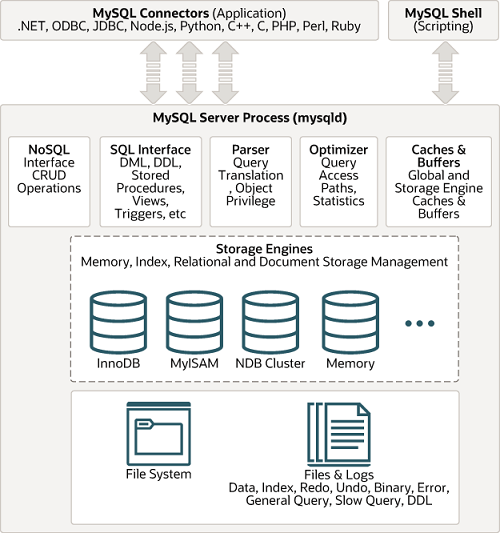
Transactions
mysql事务
mysql隔离级别
Dirty reads(脏读), Nonrepeatable reads, Phantom reads(幻读)
Isolation Levels
- READ UNCOMMITTED
- READ COMMITTED
- REPEATABLE READ
- SERIALIZABLE
MySQL’s Storage Engines
MyISAM和InnoDB
MyISAM 适合于一些需要大量查询的应用,但其对于有大量写操作并不是很好。甚至你只是需要update一个字段,整个表都会被锁起来,而别的进程,就算是读进程都无法操作直到读操作完成。另外,MyISAM 对于 SELECT COUNT(*) 这类的计算是超快无比的。
InnoDB 的趋势会是一个非常复杂的存储引擎,对于一些小的应用,它会比 MyISAM 还慢。他是它支持“行锁” ,于是在写操作比较多的时候,会更优秀。并且,他还支持更多的高级应用,比如:事务。
mysql 数据库引擎: http://www.cnblogs.com/0201zcr/p/5296843.html MySQL存储引擎--MyISAM与InnoDB区别: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008227211
Optimizing Schema and Data Types
Choosing Optimal Data Types
Indexing for High Performance
Indexing Basics
Types of Indexes
B-Tree indexes
Types of queries that can use a B-Tree index.:
- Match the full value
- Match a leftmost prefix
- Match a column prefix
- Match a range of values
- Index-only queries
Hash indexes
Indexing Strategies for High Performance
Clustered Indexes
Query Performance Optimization
Optimizing Specific Types of Queries
Optimizing LIMIT and OFFSET
Advanced MySQL Features
Character Sets and Collations
Replication
Advanced Features in MySQL Replication
Scaling MySQL
Planning for Scalability Buying Time Before Scaling Scaling Up Scaling Out Scaling by Consolidation Scaling by Clustering Scaling Back