Collections
Interfaces
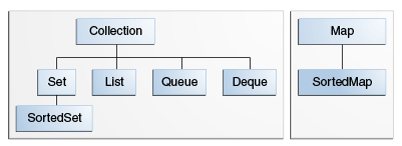
Note that all the core collection interfaces are generic. For example, this is the declaration of the Collection interface.
|
|
The Collection Interface
|
|
The Collection interface contains methods that perform basic operations, such as
int size()boolean isEmpty()boolean contains(Object element)boolean add(E element)boolean remove(Object element)Iterator<E> iterator()
It also contains methods that operate on entire collections, such as
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)void clear().
Additional methods for array operations (such as
Object[] toArray()<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
obtaining sequential or parallel streams from the underlying collection.
Stream<E> stream()Stream<E> parallelStream()
Traversing Collections
-
Aggregate Operations
Aggregate operations are often used in conjunction with lambda expressions to make programming more expressive, using less lines of code.
1 2 3myShapesCollection.stream() .filter(e -> e.getColor() == Color.RED) .forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getName()));1 2 3myShapesCollection.parallelStream() .filter(e -> e.getColor() == Color.RED) .forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getName()));1 2 3String joined = elements.stream() .map(Object::toString) .collect(Collectors.joining(", ")); -
for-each Construct
1 2for (Object o : collection) System.out.println(o); -
Iterators
1 2 3 4 5static void filter(Collection<?> c) { for (Iterator<?> it = c.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) if (!cond(it.next())) it.remove(); }
Collection Interface Bulk Operations
containsAll— returnstrueif the targetCollectioncontains all of the elements in the specifiedCollection.addAll— adds all of the elements in the specifiedCollectionto the targetCollection.removeAll— removes from the targetCollectionall of its elements that are also contained in the specifiedCollection.retainAll— removes from the targetCollectionall its elements that are not also contained in the specifiedCollection. That is, it retains only those elements in the targetCollectionthat are also contained in the specifiedCollection.clear— removes all elements from theCollection.
|
|
|
|
Collection Interface Array Operations
The toArray methods are provided as a bridge between collections and older APIs that expect arrays on input.
|
|
|
|
The Set Interface
-
HashSet
which stores its elements in a hash table, it makes no guarantees concerning the order of iteration.
1Collection<Type> noDups = new HashSet<Type>(c);1 2c.stream() .collect(Collectors.toSet()); // no duplicates -
TreeSet
which stores its elements in a red-black tree, orders its elements based on their values.
1 2 3Set<String> set = people.stream() .map(Person::getName) .collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new)); -
LinkedHashSet
which is implemented as a hash table with a linked list running through it, orders its elements based on the insertion-order.
1 2// preserves the order of the original collection while removing duplicate elements: Collection<Type> noDups = new LinkedHashSet<Type>(c);The following is a generic method that encapsulates the preceding idiom, returning a
Setof the same generic type as the one passed.1 2 3public static <E> Set<E> removeDups(Collection<E> c) { return new LinkedHashSet<E>(c); }
Set Interface Basic Operations
|
|
Note that the code always refers to the Collection by its interface type (Set) rather than by its implementation type. This is a strongly recommended programming practice because it gives you the flexibility to change implementations merely by changing the constructor.
Set Interface Bulk Operations
-
s1.containsAll(s2) -
s1.addAll(s2) -
s1.retainAll(s2) -
s1.removeAll(s2)To calculate the union, intersection, or set difference of two sets nondestructively (without modifying either set), the caller must copy one set before calling the appropriate bulk operation.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24Set<String> uniques = new HashSet<String>(); Set<String> dups = new HashSet<String>(); String[] words = {"i", "came", "i", "saw", "i", "left"}; for (String a : words) { if (!uniques.add(a)) dups.add(a); } // uniques ==> [left, came, saw, i], dups ==> [i] boolean isContain = uniques.containsAll(dups); // ==> true Set<String> union = new HashSet<String>(dups); union.addAll(uniques); // union ==> [left, came, saw, i] Set<String> intersection = new HashSet<String>(uniques); intersection.retainAll(dups); // intersection ==> [i] Set<String> difference = new HashSet<String>(uniques); difference.removeAll(dups); // difference ==> [left, came, saw] System.out.println("is contain: " + isContain); System.out.println("union words: " + union); System.out.println("intersection words: " + intersection); System.out.println("difference words: " + difference);
The List Interface
-
Positional access— manipulates elements based on their numerical position in the list. This includes methods such asget,set,add,addAll, andremove.1 2 3 4 5public static <E> void swap(List<E> a, int i, int j) { E tmp = a.get(i); a.set(i, a.get(j)); a.set(j, tmp); }1 2 3 4public static void shuffle(List<?> list, Random rnd) { for (int i = list.size(); i > 1; i--) swap(list, i - 1, rnd.nextInt(i)); }1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11import java.util.*; public class Shuffle { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String a : args) list.add(a); Collections.shuffle(list, new Random()); System.out.println(list); } }The Arrays class has a static factory method called
asList, which allows an array to be viewed as a List. This method does not copy the array. Changes in theListwrite through to the array and vice versa. The resulting List is not a general-purposeListimplementation, because it doesn’t implement the (optional)addandremoveoperations: Arrays are not resizable.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9import java.util.*; public class Shuffle { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = Arrays.asList(args); Collections.shuffle(list); System.out.println(list); } } -
Search— searches for a specified object in the list and returns its numerical position. Search methods includeindexOfandlastIndexOf. -
Iteration— extendsIteratorsemantics to take advantage of the list’s sequential nature. ThelistIteratormethods provide this behavior.1 2 3 4for (ListIterator<Type> it = list.listIterator(list.size()); it.hasNext(); ) { Type t = it.next(); ... }1 2 3 4for (ListIterator<Type> it = list.listIterator(list.size()); it.hasPrevious(); ) { Type t = it.previous(); ... }1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12String[] words = {"i", "came", "i", "saw", "i", "left"}; List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String a : words) { list.add(a); } ListIterator<String> it = list.listIterator() it.previousIndex(); // ==> -1 var ret = it.next(); // ret ==> "i" it.previousIndex(); // ==> 0 var obj = it.previous(); // obj ==> "i" it.previousIndex(); // ==> -1 it.nextIndex(); // ==> 01 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11String[] words = {"i", "came", "i", "saw", "i", "left"}; List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String a : words) { list.add(a); } public static <E> void replace(List<E> list, E val, E newVal) { for (ListIterator<E> it = list.listIterator(); it.hasNext(); ) if (val == null ? it.next() == null : val.equals(it.next())) it.set(newVal); } replace(list, "i", "e") // list ==> [e, came, e, saw, e, left]1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10public static <E> void replace(List<E> list, E val, List<? extends E> newVals) { for (ListIterator<E> it = list.listIterator(); it.hasNext(); ){ if (val == null ? it.next() == null : val.equals(it.next())) { it.remove(); for (E e : newVals) it.add(e); } } } -
Range-view— Thesublistmethod performs arbitrary range operations on the list.removes a range of elements from a
List1list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex).clear();search for an element in a range
1 2int i = list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex).indexOf(o); int j = list.subList(fromIndex, toIndex).lastIndexOf(o);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Queue Interface
The Deque Interface
The Map Interface
Object Ordering
The SortedSet Interface
The SortedMap Interface
Aggregate Operations
Algorithms
Lambda Expressions
Date-Time APIs
Deployment
How to package applications and applets using JAR files, and deploy them using Java Web Start and Java Plug-in. Preparation for Java Programming Language Certification — List of available training and tutorial resources.
Internationalization
Reflection
Middleware, server-side, or web application
JDBC Database Access
Concurrency
Standard Edition
java
-
io
- BufferedReader
- BufferedWriter
- ByteArrayInputStream
- ByteArrayOutputStream
- File
- FileFilter
- FileInputStream
- FileOutputStream
- IOException
- InputStream
- IntputStreamReader
- OutputStream
- OutputStreamWriter
- PrintWriter
- Reader
- Serializable
- StringReader
- StringWriter
-
lang
- reflect
- Field
- Method
- InvocationTargetException
- reflect
-
math
- BigDecimal
-
net
- HttpURLConnection
- URL
- URLConnection
- URLDecoder
- URLEncoder
-
nio
- charset
- Charset
- charset
-
security
- MessageDigest
- SecureRandom
- InvalidAlgorithmParameterException
- InvalidKeyException
- KeyManagementException
- NoSuchAlgorithmException
- NoSuchProviderException
-
sql
- Date
- ResultSet
- ResultSetMetaData
- SQLException
- Timestamp
-
text
- DateFormat
- DecimalFormat
- MessageFormat
- Normalizer
- NumberFormat
- SimpleDateFormat
- ParseException
-
util
-
ArrayList
-
Arrays
-
Base64.Decoder
-
Base64.Encoder
-
Calendar
-
Collection
-
Collections
-
Comparator
-
Date
-
Enumeration
-
GregorianCalendar
-
HashMap
-
HashSet
-
HashMap
-
Iterator
-
LinkedHashMap
-
LinkedHashSet
-
LinkedList
-
List
-
Locale
1formatter.withLocale(Locale.CHINESE).format(apollo11launch); -
Map.Entry
-
Map
-
Queue
-
Random
-
ResourceBundle
-
Set
-
Timer
-
TimerTask
-
TimeZone
-
UUID
-
-
concurrent
- ConcurrentHashMap
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue
- Executors
- ScheduledExecutorService
- Semaphore
- TimeUnit
- ExecutionException
- TimeoutException
-
util.logging
-
Logger
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11import java.util.logging.Logger; public class Main { private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("com.mycompany.myapp"); public static void main(String[] args) { logger.info("Logging an INFO-level message"); } }
-
-
regex
-
Matcher
-
Pattern
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25import java.io.*; import java.net.*; import java.nio.charset.*; import java.util.regex.*; try { String urlString = "http://openjdk.java.net/"; // read contents of URL InputStream in = new URL(urlString).openStream(); var input = new String(in.readAllBytes(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // search for all occurrences of pattern var patternString = "<a\\s+href\\s*=\\s*(\"[^\"]*\"|[^\\s>]*)\\s*>"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE); pattern.matcher(input) .results() .map(MatchResult::group) .forEach(System.out::println); } catch (IOException | PatternSyntaxException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
-
-
stream
- Collectors
- toSet()
- toList()
- toMap()
- joining()
- toCollection()
- summarizingInt()
- groupingByConcurrent()
- Collectors
import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Date; import java.io.Serializable;
https://docs.oracle.com/javafx/2/collections/jfxpub-collections.htm
extension
javax
- activation
- DataHandler
- MimetypesFileTypeMap
- crypto
- BadPaddingException
- Cipher
- IllegalBlockSizeException
- NoSuchPaddingException
- spec
- IvParameterSpec
- SecretKeySpec
- net
- ssl
- HostnameVerifier
- HttpsURLConnection
- SSLSession
- SSLContext
- TrustManager
- X509TrustManager
- ssl
- script
- ScriptException
- security
- auth
- login
- LoginException
- login
- auth
- xml
- bind
- Unmarshaller
- JAXBContext
- annotation
- XmlAccessType
- XmlAccessorType
- XmlElement
- XmlElementWrapper
- XmlRootElement
- XmlType
- namespace
- QName
- parsers
- DocumentBuilder
- DocumentBuilderFactory
- SAXParser
- SAXParserFactory
- soap
- SOAPBody
- SOAPBodyElement
- SOAPEnvelope
- SOAPMessage
- SOAPPart
- SOAPException
- bind
Enterprise Edition
javax
-
inject
-
Inject
Identifies injectable constructors, methods, and fields.
https://dzone.com/articles/cdi-di-p1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10public class Car { // Injectable constructor @Inject public Car(Engine engine) { ... } // Injectable field @Inject private Provider<Seat> seatProvider; // Injectable package-private method @Inject void install(Windshield windshield, Trunk trunk) { ... } } -
Named
-
-
jms
- Message
- MessageListener
- TextMessage
-
persistence
- Transient
-
servlet
- Filter
- FilterChain
- FilterConfig
- ServletInputStream
- ServletOutputStream
- ServletRequest
- ServletResponse
- ServletException
- http
- Cookie
- HttpServlet
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- HttpServletRequestWrapper
- HttpServletResponseWrapper
-
transaction
- Transactional
-
ws
- rs
- DELETE
- GET
- POST
- PUT
- Path
- PathParam
- Produces
- QueryParam
- core
- Context
- MediaType
- rs
import javax.ws.rs.GET; import javax.ws.rs.POST; import javax.ws.rs.PUT; import javax.ws.rs.DELETE; import javax.ws.rs.Produces; import javax.ws.rs.Path; import javax.ws.rs.PathParam; import javax.ws.rs.QueryParam; import javax.ws.rs.core.Context; import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19226-01/820-7627/6nisfjmk8/index.html